Trans Thoracic Biopsy (CT scan Guided Or USG Guided)
Home / Dr. Kushal Chidgupkar
Interventional Pulmonology
- Fiberoptic & Rigid Bronchoscopy
- Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) Guided FNAB & Staging
- Medical Thoracoscopy (Pleuroscopy)
- Endobronchial Stenting & Other Endobronchial Interventions
- Indwelling Pleural Catheter
- Tube Thoracostomy
- Intra-Pleural Fibrinolytic Therapy (IPFT)
- Chemical and Mechanical Pleurodesis
- Thoracentesis
- Trans Thoracic Biopsy (CT scan Guided Or USG Guided)
Trans Thoracic Biopsy (CT scan Guided Or USG Guided)
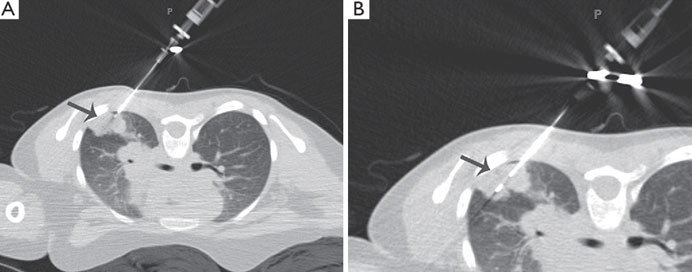
A trans-thoracic biopsy, guided either by CT (computed tomography) scan or Ultrasound (USG), is a medical procedure used to obtain tissue samples from the lungs or other thoracic structures. This type of biopsy is often performed when a lesion or abnormality is detected on imaging studies, and a tissue sample is needed for further diagnosis.
1- CT-Guided Trans-Thoracic Biopsy:
Procedure:
- The patient is positioned on the CT scanner table.
- CT scans are used to create detailed images of the target area.
- A thin, hollow needle is inserted through the skin and into the targeted lesion under CT guidance.
- Multiple samples are usually obtained for diagnostic purposes.
Indications:
- CT-guided biopsies are commonly used for lung nodules or masses, that are not easily accessible through other methods.
Advantages:
- Provides precise imaging guidance for accurate needle placement.
- Allows sampling of lesions located deep within the chest.
Complications:
- Potential complications may include bleeding, infection, or pneumothorax (air leak into the pleural space).
2- USG-Guided Trans-Thoracic Biopsy:
Procedure:
- The patient may be positioned in a specific way to optimize the ultrasound imaging.
- Ultrasound is used to visualize the lesion and guide the biopsy needle into the target area.
- The biopsy needle is inserted through the skin and into the lesion, and samples are collected.
Indications:
- USG-guided biopsies are often used for lesions that are well visualized using ultrasound, such as superficial lung lesions or chest wall masses.
Advantages:
- Real-time imaging allows for dynamic adjustment of the needle placement.
- Can be performed at the bedside in certain cases.
Complications:
- Potential complications are similar as with CT-guided biopsies, i.e. bleeding, infection, or pneumothorax.
Both CT-guided and USG-guided trans-thoracic biopsies are valuable diagnostic tools, and the choice between them depends on factors such as the location and characteristics of the lesion, as well as the expertise and equipment available at the healthcare facility.
