Intra-Pleural Fibrinolytic Therapy (IPFT)
Home / Dr. Kushal Chidgupkar
Interventional Pulmonology
- Fiberoptic & Rigid Bronchoscopy
- Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) Guided FNAB & Staging
- Medical Thoracoscopy (Pleuroscopy)
- Endobronchial Stenting & Other Endobronchial Interventions
- Indwelling Pleural Catheter
- Tube Thoracostomy
- Intra-Pleural Fibrinolytic Therapy (IPFT)
- Chemical and Mechanical Pleurodesis
- Thoracentesis
- Trans Thoracic Biopsy (CT scan Guided Or USG Guided)
Intra-Pleural Fibrinolytic Therapy (IPFT)
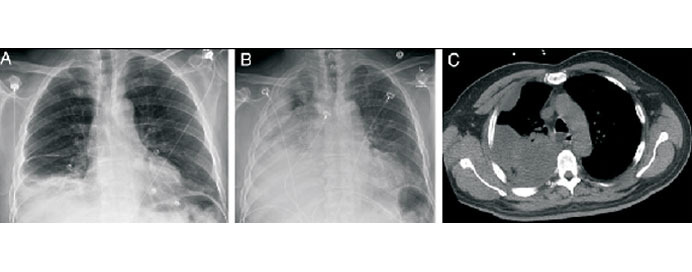
Intra-pleural fibrinolytic therapy (IPFT) is a medical intervention used in the treatment of certain pleural diseases, particularly pleural effusion and empyema. Pleural effusion is the accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space (the space between the lungs and the chest wall), and empyema is a collection of pus in the pleural space often caused by infection.
1- Purpose:
- IPFT is employed to break down fibrin strands within the pleural space. Fibrin is a protein involved in blood clotting, and its accumulation in the pleura can lead to the formation of adhesions and loculations, restricting the normal movement of the lungs within the chest cavity.
2- Procedure:
- Fibrinolytic agents, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), are instilled directly into the pleural space through a chest tube. This is often done after initial drainage of the pleural effusion or empyema.
3- Mechanism of Action:
- Fibrinolytic agents work by activating the body's natural fibrinolysis process, breaking down fibrin clots and promoting the dissolution of adhesions and loculations within the pleural space. This helps improve lung expansion and drainage of fluid or pus.
4- Indications:
- IPFT is typically considered in cases where there is fibrinopurulent pleural effusion or empyema, and conventional treatments such as drainage alone may not be sufficient.
5- Monitoring:
- Patients undergoing IPFT are closely monitored for the response to therapy, and additional imaging studies, such as chest X-rays or ultrasound, may be used to assess the resolution of pleural effusion or empyema.
6- Complications:
- While IPFT can be effective, there are potential risks and complications, including bleeding, infection, or allergic reactions to the fibrinolytic agents. Careful patient selection and monitoring are crucial to minimizing these risks.
