Endobronchial Lung Biopsy (EBLB)
Home / Dr. Kushal Chidgupkar
Interventional Pulmonology
- Thoracentesis
- Tube Thoracostomy
- Pleural Biopsy
- Chemical and mechanical Pleurodesis
- Intra-Pleural Fibrinolytic Therapy (IPFT)
- Fiberoptic & Rigid Bronchoscopy
- Medical Thoracoscopy
- Trans Bronchial Lung Biopsy (TBLB)
- Endobronchial Lung Biopsy (EBLB)
- Trans Bronchial Needle Aspiration (TBNA)
- Trans Thoracic Biopsy (CT scan Guided Or USG Guided)
- Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) Guided FNAB & Staging
- Endobronchial Stenting & Other Endobronchial Interventions
Endobronchial Lung Biopsy (EBLB)
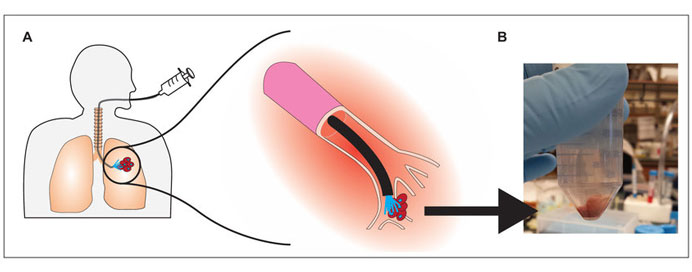
Endobronchial lung biopsy (EBLB) is a medical procedure that involves obtaining a tissue sample from the bronchial walls or lung lesions using a bronchoscope. The bronchoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera that is inserted through the nose or mouth and into the airways.
1- Indications:
- EBLB is often performed when there is a need to investigate abnormalities within the bronchial walls or lesions in the lungs.
- It can be used for diagnosing conditions such as lung infections, inflammatory lung diseases, or lung cancers.
2- Procedure:
- The patient may receive local anesthesia or sedation to help relax during the procedure.
- The bronchoscope is inserted through the nose or mouth and guided through the trachea and bronchi to the target area.
- Biopsy forceps or other tools are passed through the bronchoscope to obtain small tissue samples from the bronchial walls or lung lesions.
3- Biopsy Types:
- EBLB can include different types of biopsies, such as transbronchial biopsy (sampling from the bronchial walls) or endobronchial biopsy (sampling from within the bronchial tree).
- Fluoroscopy or guided imaging may be used to navigate the bronchoscope to specific areas of interest.
4- Analysis:
- The collected tissue samples are sent to a pathology lab for microscopic examination. This helps in determining the presence of abnormalities, including infections, inflammation, or cancer cells.
5- Complications:
- EBLB is generally considered a safe procedure, but potential complications may include bleeding, infection, or respiratory distress.
- Careful monitoring during and after the procedure helps minimize these risks.
6- Post-Procedure Care:
- After the biopsy, patients are typically monitored for any immediate complications and may be observed for a short period before being discharged.
